This week, Pakistan’s stock market continued its bull run and reached a record-high level of 50,000 points, last achieved 6 years ago on 8th June, 2017. But why did this happen?
The financial markets are complex and ever-changing, influenced by a myriad of factors. Understanding these market cycles and knowing how to invest in various market environments can significantly impact your investment success. Below, we’ll explore the different phases of market cycles and provide insights on how to navigate each phase effectively.
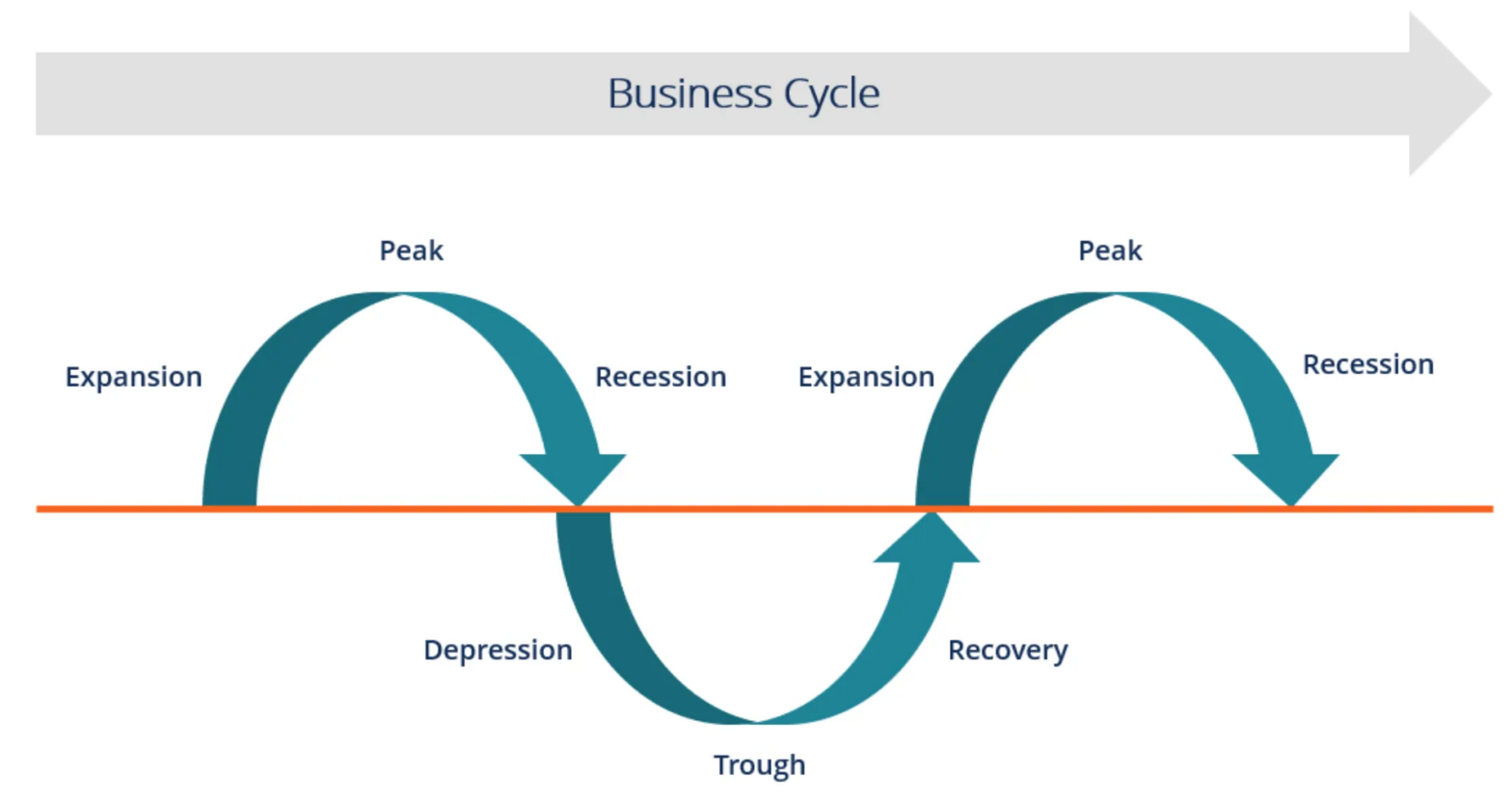
Step 1: Identifying Market Cycles
Market cycles are a natural part of the financial landscape, characterized by recurring patterns of growth, stability, decline, and recovery. These cycles are driven by economic conditions, investor sentiment, and various other factors. The four primary phases of a market cycle are:

1. Expansion
This is the phase where the economy is growing, and stock prices are on the rise. It’s a period of optimism, increasing employment, and strong corporate profits. Investors tend to be confident, and risk appetite is high.
2. Peak
At the peak of a market cycle, things may seem rosy, but it’s also a time of vulnerability. Stock prices may be at their highest point, and euphoria can lead to excessive risk-taking. This phase precedes a downturn.
3. Contraction
The contraction phase, often referred to as a bear market, is marked by declining stock prices, economic challenges, and pessimism. Fear and uncertainty drive investors to adopt a more cautious approach.
4. Trough
The trough represents the bottom of the cycle, where the economy stabilizes and stock prices reach their lowest point. It’s a period of despair and capitulation, but it also sets the stage for the next expansion phase.
Understanding these phases is crucial for investors. The key is to adapt your investment strategy to each phase of the cycle.
Investing in Different Market Environments
1. Expansion Phase
- Diversification

In this phase, it’s essential to have a diversified portfolio. Consider investing in a mix of stocks, bonds, and other assets to spread risk.
- Growth Stocks

Growth stocks tend to perform well in expansion phases. These are shares of companies that are expected to grow faster than the market average.
- Regular Review
Continuously review your portfolio, rebalance it if necessary, and consider taking profits.
2. Peak Phase
- Risk Management

As stock prices peak, it’s a good time to reassess your risk tolerance. Consider reducing your exposure to equities and reallocating to more conservative investments.
- Dividend Stocks
Dividend-paying stocks can provide stability during a market peak, as they often continue to pay dividends even when stock prices decline.
- Cash Reserves
Building a cash cushion can be prudent for future opportunities.
3. Contraction Phase
- Stay Calm
Avoid panic selling. Market downturns are a natural part of the cycle, and history has shown that they are followed by recoveries.
- Quality Investments

Focus on quality assets, such as blue-chip stocks and government bonds. These tend to be more resilient during economic downturns.
- Rebalance
Rebalance your portfolio to maintain your target asset allocation.
4. Trough Phase
- Opportunistic Investing
As the economy starts to recover, consider increasing your exposure to riskier assets, as they often offer attractive valuations.
- Value Stocks

Value stocks, which are undervalued relative to their fundamentals, can perform well during the early stages of a recovery.
- Long-Term Perspective
Keep a long-term perspective and stay patient. The recovery phase can be volatile, but it also presents significant opportunities.
Adapting your investment strategy to different market environments is essential for long-term success. If we understand the natural cycle of an economy, we are better prepared for the changes to come. By staying informed and making prudent investment decisions, you can navigate the complexities of the financial markets effectively.